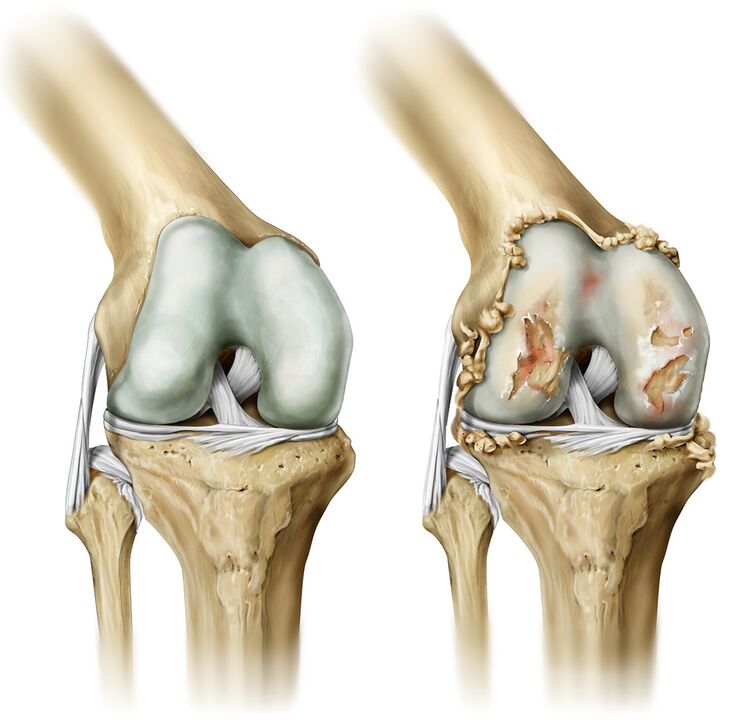
Arthropathy of the joints is a chronic disease characterized by degenerative changes in articular cartilage, resulting in bone tissue deformation. The joints of the big toe, hip and knee are most commonly affected.
Symptoms of the disease
- The first clinical symptom of arthropathy is pain in the affected joint during excessive physical exertion. Pain may occur during exercise. As the disease progresses, joint pain can bother a person even at rest and cause insomnia.
- Bite the joints. Due to the destruction of the cartilage layer, the bones will rub, and when they move in the joints, you will hear clicks and crunches. As the disease progresses, the degree of austerity increases.
- Declining liquidity. If the joints are damaged, movement is restricted, severe arthropathy, the patient's limbs are stiff in the morning.
- Joint deformities. Without adequate and timely treatment, joints will deform and their appearance will change.
- As the inflammatory process intensifies, the sensitivity of the patient's toes decreases and the fingertips become numb.
Cause
The main reason for the development of arthropathy is the growth of the cartilage layer between joints and bones. The contributing factors are:
- Strenuous physical activity;
- Minimally invasive joints;
- Frequent fractures
- Wear tight shoes or high heels
- Congenital tendency.
diagnosis
The main method of diagnosing joint disease is to carefully collect the patient's medical history (professional medical history).
The diagnosis is based on examination of the patient and other studies, including joint X-rays, arthroscopy, ultrasound, MRI, and computed tomography.
- Ultrasound. This research method is reliable and harmless. Since ultrasound diagnosis refers to a non-invasive method, this study has no contraindications. With the help of ultrasound, it can diagnose cartilage tissue thinning, joint meniscus degenerative changes, joint membrane thickening, and whether there is fluid in the joint cavity. This research will enable you to accurately choose the treatment method for joint disease.
- MRI and computed tomography. With the help of computed tomography and MRI, the condition of the joints can be assessed: the thickness of cartilage, whether there are erosions or cysts in the bone tissue, to determine the amount of intra-articular fluid.
- Arthroscopy. This study is more commonly used to determine the cause of the development of joint disease.
complication
Without timely medical care, arthropathy will develop and complications may occur, such as:
- Inflammation of the tissues around the joints;
- Limited movement of affected joints;
- Degenerative changes in the hip joint;
- Change the shape of the joints.
Treatment of disease
The patient is treated according to the degree of joint damage. The treatment of joint disease begins with pain relief.
While taking analgesics, the patient was also prescribed anti-inflammatory drugs. In addition to medication, the patient has to receive a course of physical therapy.
Massaging the affected limbs after the acute inflammatory process subsides can reduce pain, normalize joint activity, and relieve muscle spasms.
Physical therapy exercises are designed to relieve muscle stiffness, warm the muscles and enhance the general condition of the patient. Exercise helps maintain correct posture and a steady gait.
Convalescent treatment is suitable for stable remission. Mud baths, applications, and other procedures help restore the motor function of the joints and relieve pain.
If conservative treatment does not bring the expected results, surgical joint replacement is prescribed for the patient. The endoprosthesis is made of materials that will not be rejected by the human body. They allow you to fully restore the physiological functions of the affected joints.
Unique treatment method: radiofrequency ablation and destruction of the integrity of the method by destroying the integrity of the nerve that causes pain.
Risk Group
The risk group includes the following people:
- overweight;
- Varicose veins;
- athlete;
- pianist;
- programmer.
prevention
Prevention of joint disease is as follows:
- Good nutrition;
- Prevent injuries and fractures;
- Limit the load on joints with genetic predisposition;
- Weight control
- Wear well-fitting shoes.
Diet and lifestyle
Due to the genetic predisposition to the development of joint disease, and during the worsening of the disease, it is necessary to adjust diet. It is recommended to add sea fish (sardines, salmon, tuna), fresh vegetables and fruits, and grains to the diet. Limit baked goods, fatty meat, chocolate and alcohol.
It is recommended to stay in fresh air and avoid exposing the joints to increased physical activity.